Infrared thermometer mainly consists of optical imaging scanning system, photodetector, signal amplifier, signal processing and display output. The working principle is as follows: The optical imaging scanning system can collect the infrared radiation energy of the target object in the field of view, and the focused infrared radiation energy falls on the photodetector and is transformed into an electric signal. The electric signal passes through an amplifier and a signal processing circuit. , and after a series of signal processing and emissivity correction, you can display the measured target temperature. Figure 1: Block diagram of infrared thermometer Two kinds of infrared radiation thermometers (1) Monochromator: A monochromatic thermometer is proportional to the amount of radiation in the band. (2) Two-color thermometer: The two-color thermometer is proportional to the ratio of the radiation in the two bands. Infrared Thermometer's usual advantages (1) Convenient: The temperature can be quickly measured, and the temperature of all the connection points can be read. In addition, the infrared thermometer is solid, lightweight, and portable. (2) Accuracy: Usually the accuracy is within 1°C, and small changes in temperature can be quickly and accurately detected. (3) Safety: The inaccessible or unreachable target temperature can be safely and non-contactly read, and the target temperature can be read within the allowable range of the instrument. Using Infrared Thermometer Precautions (1) Infrared thermometers can only measure the surface temperature of an object and cannot measure the internal temperature of an object. (2) The temperature cannot be measured by quartz glass. The glass has very special reflection and transmission characteristics. For surface bright or polished metal objects, such as stainless steel, aluminum, etc., the measurement accuracy is not accurate. (3) It is necessary to shorten the measurement distance as much as possible to prevent signal attenuation. The thermometer is aimed directly at the target and the target is scanned up and down until a hot spot is determined. (4) Avoid environmental factors such as steam, dust, and smoke that affect the optical system of the thermometer and reduce the measurement accuracy. (5) Take care to eliminate the influence of ambient temperature. If the thermometer is suddenly exposed to a temperature difference of 20°C or more, allow the instrument to adjust to the new ambient temperature within 20 minutes.
The principle of infrared radiation thermometer 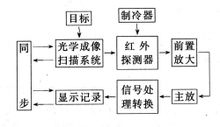
Infrared thermometer detailed introduction
In theory, any object in nature with a temperature above 0 K (-273.16 °C) at absolute zero will constantly emit infrared radiation energy to the surrounding space. The size of the infrared radiation energy of the object mainly depends on the surface temperature of the object. Therefore, by detecting the infrared energy emitted by an object, the surface temperature of the object can be accurately measured.